Expert Advice on Trinity Boring Solutions
Horizontal Directional Drilling Methods: A Comprehensive Guide for Contractors
Directional drilling approaches signify a vital advancement in underground construction. These techniques enable efficient utility installations with limited surface disruption. Contractors should navigate numerous challenges, including equipment selection and soil conditions. Acknowledging the importance of safety and real-time monitoring can greatly impact project outcomes. Grasping these factors is essential for successful implementations. However, the complexities of the process and emerging technologies raise further questions that require exploration.
Comprehending Directional Boring: The Basics
Horizontal directional drilling, a crucial method in contemporary construction and utility installation, allows contractors to create underground pathways with limited surface disruption. This technique involves drilling a hole underground using specialized equipment, which is guided along a predetermined path. Unlike traditional trenching methods, directional boring lessens the impact on the surrounding environment, making it ideal for urban areas and sensitive landscapes.
This process commences with a pilot hole, which is bored using a rotating drill bit. Once the pilot hole is completed, a reamer is fitted to enlarge the bore to the correct diameter for the utility installation. This technique is especially valuable for installing pipes, cables, and conduits underneath roads, rivers, and other impediments. Understanding the principles of directional boring provides contractors with the knowledge to properly design and execute projects while following safety regulations and environmental considerations.
Important Equipment for Guided Boring
Successful directional boring requires a variety of specialized equipment designed to ensure precision and efficiency during the drilling process. Essential to this operation is the directional drilling machine, which allows operators to drill at varying angles and depths while maintaining accuracy. Additionally, drill bits tailored for specific soil conditions are vital, as they influence the cutting efficiency and overall performance.
A further essential element is the tracking system, which provides real-time data on the drill's location and trajectory, making certain that the bore path remains accurate. Mud pumps and drilling fluid systems are likewise vital, as they support cooling and lubrication while eliminating cuttings from the borehole. Additionally, ancillary tools such as reamers and swivels increase the capabilities of the primary equipment, allowing contractors to deal with diverse underground conditions. Combined, this equipment forms the core of effective and successful directional boring operations.
Critical Strategies for Professional Directional Boring
Profitable directional boring depends on appropriate equipment selection and a comprehensive assessment of soil conditions. Contractors must select the right tools find details about tailored to specific project requirements to maintain efficiency and safety. Furthermore, understanding the soil type and its characteristics can greatly influence the boring process and overall project outcomes.
Strategic Equipment Selection
Picking the right equipment for directional boring is vital for contractors aiming to improve efficiency and effectiveness on the job site. A detailed analysis of the project's scope and specific requirements guides the selection process. Key factors include the size and type of the drilling machine, which should match the diameter and depth of the borehole. Additionally, contractors must assess the necessary drill bits and accessories, ensuring compatibility with the chosen equipment. It is also important to take into account the power source and mobility of the machinery, as these factors affect operational efficiency. Lastly, investing in advanced technology, such as locating systems, can increase precision and reduce costly mistakes, finally leading to successful project completion.
Earth Condition Assessment
Evaluating soil characteristics is an essential component in the directional boring process, as it directly affects the choice of techniques and equipment used. Contractors must evaluate the soil's composition, moisture content, and density to determine the practicality of the project. Techniques such as visual inspection, soil sampling, and geotechnical testing are applied to gather essential information. Understanding soil types—whether clay, sand, silt, or gravel—helps predict how the ground will perform during boring. Additionally, identifying potential obstacles like rocks or groundwater can prevent costly delays. Accurate assessments lead to informed decisions, ensuring that the right boring methods and machinery are used, ultimately enhancing efficiency and reducing the risk of project failure. Proper soil evaluation is, consequently, paramount for successful directional boring operations.
Safety Elements in Directional Boring
Even though directional boring provides effective solutions for underground installations, it introduces particular safety challenges that contractors must address. As a primary concern, operators should carry out detailed site assessments to detect potential hazards, like underground utilities and unstable soil conditions. Proper training and following safety protocols are critical to mitigate risks related to equipment operation and personnel safety.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is necessary on location, such as hard hats, gloves, and eye protection. Furthermore, upholding clear communication among team members guarantees that all personnel understand their surroundings and potential risks. Contractors should also establish a complete emergency response plan, prepared to handle any incidents that may emerge.
Consistent equipment maintenance and inspections boost operational safety, decreasing the likelihood of mechanical failures during boring operations. By focusing on these safety protocols, contractors can ensure the safety of their workforce and achieve successful project completion.
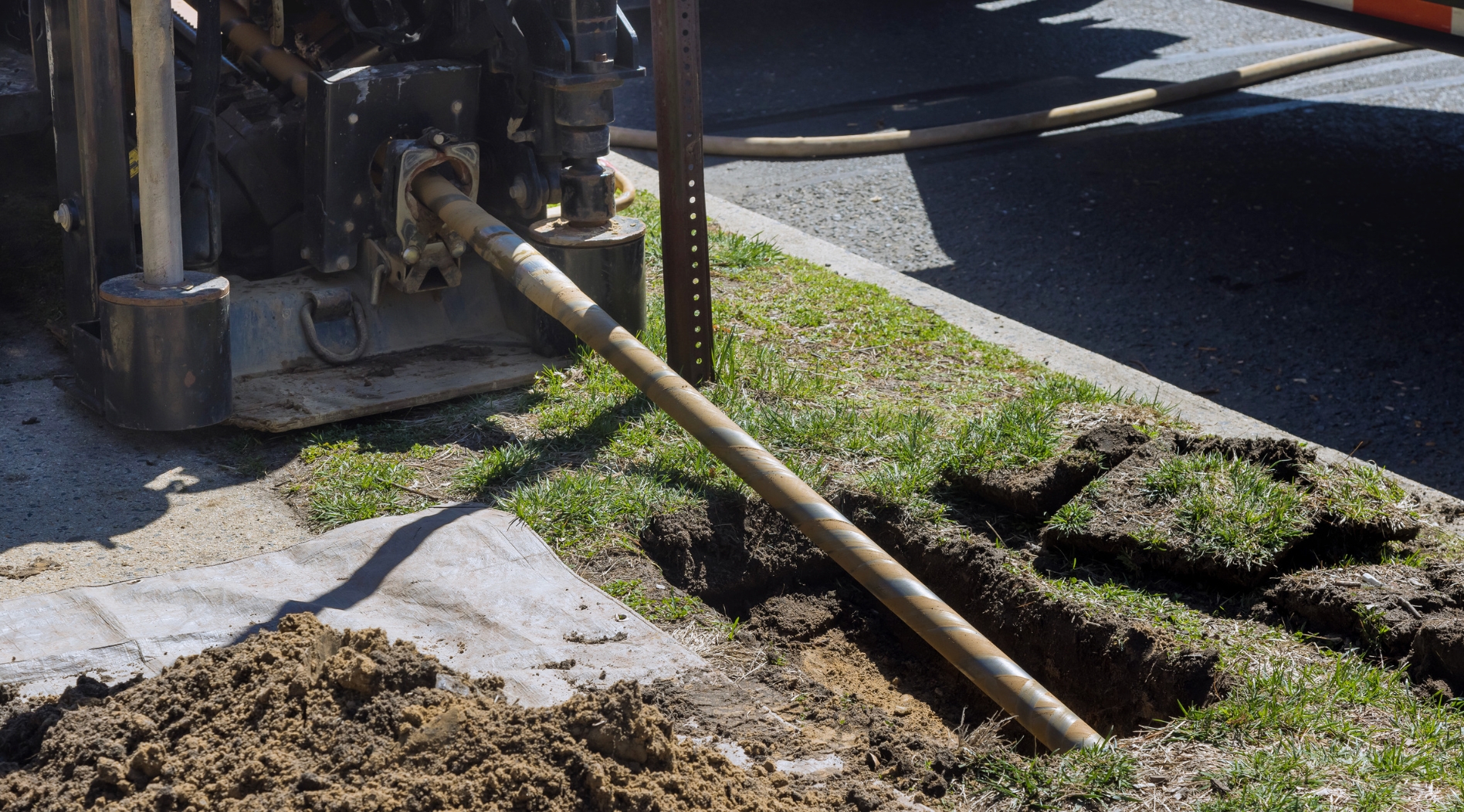

Typical Applications of Directional Boring
Directional boring is commonly used across multiple industries for its ability to install utilities and infrastructure underground with minimal surface disruption. One popular application is in the installation of water and sewer lines, where traditional trenching methods can be costly and disruptive. Directional boring enables precise placement of these lines, decreasing the impact on nearby landscapes.
Telecom companies regularly use directional boring to lay fiber optic cables, delivering fast and efficient internet service without significant excavation. Additionally, electric utility providers use this technique for the installation of conduits for power lines, improving reliability and safety.
Directional boring is also beneficial for environmental projects, such as installing monitoring wells or remediation systems, as it minimizes ground disturbance and preserves natural habitats. Ultimately, the multifunctionality and performance of directional boring designate it as an indispensable solution for different utility implementations and construction endeavors.
Troubleshooting Typical Problems in Directional Boring
Directional boring presents multiple challenges requiring contractor intervention for guaranteed project success. Standard difficulties consist of malfunctioning equipment, problematic soil conditions, and pipeline alignment concerns. Comprehending these challenges and their remedies is crucial for preserving efficiency and reducing downtime.
Equipment Issues and Resolutions
Equipment failures can interrupt the effectiveness of any directional boring project, bringing about delays and elevated costs. Standard issues include hydraulic failures, drill bit wear, and misalignment. Hydraulic failures frequently arise from leaks or pressure drops, which can be rectified by verifying connections and replacing damaged components. Drill bit wear calls for regular inspections; replacing worn bits promptly maintains peak performance. Misalignment can arise from improper setup or navigation errors, and can be remedied by recalibrating the equipment and securing proper operator training. Establishing a routine maintenance schedule is crucial for preventing malfunctions. Additionally, keeping spare parts on hand can limit downtime, permitting contractors to respond rapidly to unexpected equipment issues and maintain project timelines successfully.
Ground Conditions and Approaches
Soil properties play an essential role in the success of any directional boring project, presenting a variety of challenges that contractors must navigate. Diverse soil types, such as clay, sand, or rocky formations, can affect drilling efficiency and tool wear. In addition, high water tables may create unstable conditions, making more difficult the bore path. To tackle these challenges, contractors can carry out thorough site surveys and soil analyses before initiating work. Employing appropriate drilling fluids can also help maintain borehole stability and lower friction. Installing real-time monitoring systems allows for immediate adjustments to drilling parameters, increasing overall performance. By anticipating potential soil-related issues, contractors can establish effective strategies that ensure a smoother directional boring process and reduce costly delays.
Pipeline Alignment Corrections
Misalignment of pipelines during directional boring can cause significant complications and delays in project timelines. To address this issue, contractors can employ several corrective measures. First, accurate pre-bore surveys are vital to identify potential alignment difficulties before drilling begins. If misalignment happens, using a reaming operation can help adjust the bore path to align with the intended pipeline route. Furthermore, employing advanced tracking systems during the boring process enables real-time adjustments. In cases of severe misalignment, contractors may need to excavate sections of the bore for manual realignment. In conclusion, thorough post-installation inspections verify the pipeline meets required specifications, mitigating the risk of future misalignment issues. These strategies enhance the overall efficiency and success of directional boring projects.
Upcoming Developments in Directional Boring Technology
With the growing demand for efficient underground construction methods, the future of directional boring technology is ready for significant advancements. Innovations are projected to emphasize automation and real-time data analytics, enhancing precision and efficiency during installations. The introduction of advanced materials will likely strengthen the durability and performance of drilling equipment, lowering maintenance costs and downtime.
Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms will facilitate improved decision-making during complex projects, improving drilling paths and reducing environmental impact. Furthermore, the development of compact and smaller machinery will enable access to urban and congested areas, expanding the applicability of directional boring.
Eco-consciousness will also play an important role, with heightened emphasis on environment-conscious practices and techniques that lower noise and energy consumption. All in all, these trends point to a progressive shift towards greater efficient, effective, and environmentally responsible directional boring methods in the coming years.
FAQ
What Permits Are Needed for Directional Boring Projects?
Directional boring projects typically require various permits, including excavation permits, environmental permits, and utility location permits. Area-specific regulations may fluctuate, demanding coordination with municipal agencies to confirm compliance with all mandatory legal prerequisites before starting.
How Do I Select the Right Contractor for Directional Boring?
To choose the right contractor for directional boring, one should evaluate their experience, review references, confirm licensing and insurance, assess equipment quality, and compare project bids to guarantee a dependable and economical partnership.
What Are the Environmental Effects of Directional Boring?
Directional boring can lead to soil disturbance, the risk of groundwater contamination, and damage to local ecosystems. However, when executed appropriately, it decreases surface disruption and can be a greener alternative to typical excavation methods.
How Do Weather Factors Affect Directional Boring Operations?
Weather factors greatly impact directional boring operations, as intense rainfall can cause soil instability, while harsh thermal conditions may influence equipment performance. High winds and electrical storms also introduce safety hazards, potentially halting or delaying the work.
How Much Do Directional Boring Services Usually Cost?
The typical price for directional boring services generally falls from $5 to $15 per foot, based on factors such as project complexity, soil conditions, and local market rates, influencing overall pricing for both contractors and clients.